
Almanac
French Republic

Surgeon General
MGA Jacques MARGERY, MD
Directeur central du Service de santé des armées
Main Task of the French Military Medical Service
The main mission of the French Military Medical Service (FMMS; in French, Service de santé des armées - SSA) is to provide Armed Forces with medical support anywhere in the world, any time and under any circumstances.
Structure
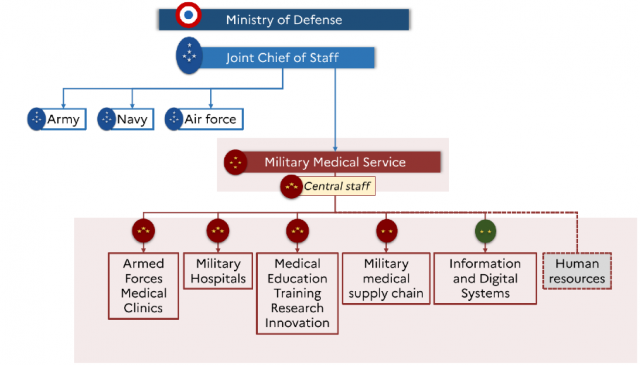
The French Military Medical Service (FMMS) is a fully joint service, placed under the authority of the Armed Forces Joint Chief of Staff. Its headquarters are located in Paris, since 2015: Balard (south-west of Paris) and historically in Vincennes (east of the Capital). The FMMS structure covers five fields:
- armed forces medical clinics;
- military hospitals;
- medical education, training, research and innovation;
- military medical supply chain;
- information and digital systems .
They are organised through directorates, supported by a human resources department. All focus on the main mission of the FMMS: to provide Armed Forces with medical support anywhere in the world, any time and under any circumstances.
Source: Ministry of Defence French Republic
Central Staff
The central staff includes three deputies (operations, medical defence strategy and resources support). They advise the surgeon general on their field of expertise.
The armed forces center for epidemiology and public health (CESPA) is directly subordinated to the Central Staff. Its mission is to implement public health policies within the French Defense community. The CESPA is divided into 6 specific departments:
- the military health intelligence department whose mission is to identify potential health risks and threats to the armed forces;
- the health surveillance and investigation department that monitors the health of the armed forces and performs investigations of health events;
- the epidemiological surveys department that is responsible for clinical and epidemiological surveys among the armed forces;
- the health promotion, prevention and programs department whose mission is to develop health education and evaluation of projects;
- the pest and vector department, which is responsible for the vector control and the mitigation of the vector-borne diseases among armed forces;
- the modelling, biostatistics and data science department, which is in charge of the development of new technologies for health projects.
Public health is a large field, at the crossroads of several medical specialities and social sciences. Hence, CESPA works on several topics, on communicable diseases such as malaria, arboviruses, diarrhoea or sexually transmitted infections; but also non-communicable diseases like post-traumatic stress disorders, addictions, or physical injuries due to military or sports training. CESPA also takes part or organizes several training courses for civilian and military students in partnership with French universities and international bodies like the NATO Centre of Excellence for Military Medicine. It also takes part in several NATO expert committees to produce guidelines in its areas of expertise. Finally, CESPA has developed international collaborations with several organizations notably with NATO.
The Armed Forces’ Medical Directorate (DMF)
The armed forces medical directorate supports and commands 16 Regional Medical Centers, 3 specific medical services (naval action force medical service, submarine forces medical service, special forces medical service), and the military radiation protection service (Service de Protection Radiologique des Armées – SPRA). Covering the whole territory, the armed forces medical clinics are also active overseas, onboard navy ships and beside the French troops deployed abroad. The military personnel who works in these medical clinics is regularly deployed oversea or on the national territory to provide medical support to operational engagements. The regional medical centers are organized into several armed forces medical clinics spread over a region, which allows each military unit to be supported with close primary healthcare. Their mission is to ensure the operational readiness of deployable armed forces, offer medical expertise and advice to the units commanding officers, while preparing themselves to deployments.
The Military radiation protection service (Service de Protection Radiologique des Armées – SPRA)
The French military radiation protection service was established in 1973. It provides technical support of military units in the area of radiation protection. It is located within Percy Military Hospital premises, which is a trauma center for military and civilian emergencies (trauma center). The SPRA has 85 military and civilian employees. Since 2005, it is charged with providing occupational medicine, especially the medical and radiobiological supervision of personnel exposed to ionizing radiations in the French Ministry of Defense; hygiene and safety (expert technical controls in facilities); regulation; education (conducting about 1 000 hours of training courses per year) and intervention in the case of a radiological incident. On behalf of the French Military Medical Service, the SPRA has concluded agreements with the French Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), EDF Group (Electricité de France), ORANO group, and the French Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Institute (IRSN) to provide the best medical care for radiation-related victims. The SPRA works with Percy Military Hospital to organize radiobiological training and exercises, especially with Percy’s surgical unit and the center for the treatment of radio-contaminated wounded (CTBRC). The SPRA advises the headquarters and supports local medical services during the exercises performed by the French Navy or Air Force.
Military Hospitals Directorate (DHOP)
The component of the FMMS is going through a major reorganization (SSA 2020 Project) to challenge its activity within the framework of the Ambition 2030 project who will be more oriented towards its operational purpose.
Within this framework, two complexes of military teaching hospitals (Ensembles Hospitaliers Militaires - EHM), one in the Paris area (Percy and Begin hospitals), served by Villacoublay airbase and the other in the Toulon-Marseille area (Laveran and Saint Anne hospitals) served by Istres airbase, constitute four trauma centers also competent in infectious diseases.
Additionally, the FMMS has four other military hospitals with a high level of military-civilian integration (Ensembles Hospitaliers Civilo Militaires – EHCM): in Bordeaux, Brest, Metz and Lyon. Their field of expertise is supported by a high level of intensive care and surgery departments integration with the civilian hospitals, the rehabilitation of physical and mental injuries, the response to a sanitary crisis, the participation of several armed forces medical clinics in relation with emergency military hospitals units and common civilian-military management as well. Since 2015, several major events have prompted the FMMS to tighten significantly its cooperation with the Ministry of public health concerning specific training (war surgery in national territory, military medical support to the civilian population, health crisis). The military hospitals have become a key stakeholder in this cooperation. Having in mind the primary mission of supporting the French armed forces during operational engagements, the French military hospitals are in line to fulfil the French ministry of defense objective is to dispose of a capacity 65 deployable surgical teams in 2025 on all operations abroad.
The recent epidemiological crisis of Covid-19 virus has shown the importance of the FMMS’s contribution to public health as part of the Health-Defense protocol.
Medical education/training, research and innovation directorate (DFRI)
The Education/Training and research directorate is the overarching structure of the three military medical schools and the research center (IRBA). The three schools ensure the medical studies and the continuous improvement of military medical skills: the “Ecole de santé des armées” and the “Ecole du personnel paramédical des armées” both colocated in Lyon and the “Ecole du Val-de-Grâce” in Paris. The IRBA is in charge of conducting research programs.
L’Ecole de santé des armées (ESA)
The Military Medical School in Lyon-Bron was inaugurated on 1st of July 2011 after the merging of their predecessors published in Bordeaux and Lyon. The global mission of the military medical corps comprises four main steps regarding academic education and professional training for physicians. We help our cadets to become high standards practitioners throughout their time at university by providing them with all the logistic and scientific means they need. They follow in parallel a military training to acquire the skills and abilities that officers must possess. They are also trained to provide medical and urgent care in challenging environments including on the battlefield under the enemy fire. This represents an 1800-hours course delivered over the six years of their medical curriculum. Once this course is completed, they are awarded a professional master in addition to their medicine doctorate.
During this intense program, the cadets learn the three-hundred-year-old traditions of the medical corps, which they will then perpetuate and promote wherever they will be deployed. The academy fulfills the difficult task of shaping tomorrow’s military physicians so that they may practice the medical art in austere environments and international allied coalitions.
L’Ecole du personnel paramédical des armées (EPPA) (The Military Nursing School)
In collaboration with the civilian University and the nurse education institutes, the education provided by the Military Paramedical School gives to all students, the official qualification for paramedical specialities. The basic military education, and the specific courses are given at the same time, prepare them for operational missions in military contexts. The training of nurses and nursing assistants are given in civilian education institutes in Lyon in the same way that medical military students are trained in civilian medical universities.
L’Ecole du Val-de-Grâce (EVDG)
Born on 1st October 2005, the Val-de-Grâce School (The French Military Medical Academy) is the heir to the Ecole d’Application du Service de Santé des Armées. Its aim is firstly to supervise the last years of medical training of the military students. To do so, the Val-de-Grâce School works closely with the military hospitals and any military medical facility that provides training. Moreover, it organizes further education for physicians, pharmacists, veterinarians, dentists and administrative officers, adapted to their missions. It also provides ongoing training of officers in active duty or reservists, nurses and specialized paramedical technicians, as well as foreign students. Finally, it runs the digital distance-learning platform for the whole FMMS.
For all these actions, the school relies on its 108 associated professors in 10 medical specialities. Located in Paris, the prestigious setting allows the organizations of many military medical or scientific events, even cultural ones.
The Armed Forces Biomedical Research Institute (IRBA)
The IRBA is in charge of conducting research programs the French Military Medical Service required to support the French armed forces in the biomedical domain. It also delivers consultation, education and training in specific areas (e.g. CBRN defense, aeromedical training). The aim is to improve human protection from environmental and human factors constraints of operations, to improve biomedical knowledge on the different CBRN threats and develop the up-to-date relevant medical countermeasures and to identify new therapies and healthcare procedures for battlefield injuries and diseases. IRBA operates several national reference laboratories (NRL), (orthopoxvirus, Bacillus anthracis, arbovirus, and associated NRL for malaria). Created in 2009 by merging the various SSA research centers and institutes into a unique structure. IRBA is located South of Paris but still has distant units: in Marseille (NRL for arbovirus and parasitology/entomology unit and associated NRL for malaria), in Toulon (research and consultation for the maritime environment), in Mont-de-Marsan (aeromedical technical consultation) and within the Armed Forces Blood Transfusion Centre in Clamart). Together with state-of, the art scientific equipment, this location, close to headquarters and military hospitals as well as to major universities and research centers, puts IRBA in a key network to perform its missions. A large set of interactions is built with military/civilian, scientific/operational partners that leverage IRBA own resources and provide a vivid community to address Defense and Security biomedical challenges for military purpose.
The Armed Forces Drugs and Material Directorate (DAPSA)
The armed forces drugs and material directorate (DAPSA), settled in Orléans, heads the 6 specialized centers which constitute the military medical supply chain (MMSC). The DAPSA declines and conducts the strategy and politics decided by the FMMS Command. The 6 specialized centers are:
- a purchasing and finance platform (PFAF-Santé) in charge of awarding public contracts and paying invoices for the benefit of the MMSC and each establishment of the French military health service (SSA);
- two armed forces drugs and material centers (ERSA) settled in Vitry-le-François and in Marseille are in charge of storing, maintaining and delivering the drugs and equipment;
- the armed forces pharmaceutical center settled in Orléans (PCA) is both a pharmaceutical R&D laboratory and a factory. It is in charge of developing and manufacturing medicines and medical countermeasures against CBRN threats;
- the armed forces medical material development and maintenance center (ECMSSA) settled in Orléans is the engineering center for biomedical equipment. It is in charge of developing and storing military medical concepts such as readymade rapidly deployable medical facilities;
- the armed forces blood transfusion center (CTSA) settled in Clamart deals with blood products such as plasma, platelets and blood cells (detailed description follows).
Armed Forces Blood Transfusion Centre (military blood institute)
The main mission of the Armed Forces Blood Transfusion Centre (Centre de Transfusion Sanguine des Armées) is to provide quality blood products wherever and whenever needed, in any circumstances, to all military services. To achieve this mission, CTSA ensures the collection, the processing, the storage, the distribution of every type of blood product. Due to the specific constraints of providing blood supply overseas, CTSA focuses on the production and availability of specific blood products such as the freeze-dried plasma (PLYO) or the fresh whole blood collection and transfusion kit. At the same time, in addition to a 24/7 advice by phone, the CTSA provides educational training to every health-care worker who is supposed to face war casualties or more generally blood transfusion. In coordination with hematology and other clinical departments, the CTSA manages patients needing therapeutic apheresis, stem cell collection, or transfusions during long-term therapy. To complete its activities, CTSA ensures product banking for cell and tissue therapy. Finally, CTSA is invested in research and development (focused on advanced therapy medicinal products, mesenchymal stem cells, etc.) to maintain its expertise and always provide the best blood products regarding efficiency, safety and ease of use.
The information and digital systems directorate
The information and digital systems directorate (DSIN) of the FMMS was officially created on the third of September 2018 to simplify the governance of the communication and information systems (CIS) function within the medical branch.
Thus, the CIS was unified through the creation of this decentralized directorate, to integrate the local levels (until then delegated to the establishments) and to participate in the decision-making process at strategic level.
The Information and Digital Systems Directorate functions at both strategic and operational levels; therefore, it is in charge of proposing the IDS policy and of implementing it in an operationally manner.
Finally, as a decentralized directorate, it fulfills the role of budget management and guarantees the performance of the IDS function.
(status: 18 June 2025)











