
Article: M. BOHONEK (CZECH REPUBLIC)
Concept of Blood Supply in the Army of the Czech Republic
New Field Transfusion Unit
The availability of sufficient blood is a crucial issue of military medical service, because exsanguinating hemorrhage is the major cause of death in military operations. In 2011 – 2013, the Army of the Czech Republic has developed a special field transfusion unit (FTU) that integrates all known and accessible possibilities of blood and blood products supply. The ACR FTU, together with the ACR field lab unit, is currently the most complex solution for securing a healthy supply of blood and blood products during field operations within the NATO countries.
Introduction
Blood substitution and blood supply are permanent strategic and logistic problems of military medical services across the world arising from the blood, which is a biological drug, and has a limited shelf life and needs a special transport conditions. The availability of sufficient blood is the crucial issue of military medical service, because exsanguinating hemorrhage is the major cause of death in military operations. The blood supply concept of the Army of the Czech Republic (ACR) field hospitals operating in foreign missions was based on the periodic delivery of blood products (BP), usually in 4-5 week intervals with use of supply flights. Delivered BP, red blood cells (RBCs) and fresh frozen plasma (FFP) were stored in the carry-on serving storage (cooling and freezing box) of the container unit BHL-FH (biochemical and hematological laboratory of the field hospital).
 Deployed Field Transfusion Unit (FTU)
Deployed Field Transfusion Unit (FTU)
Based on long-term experience evaluation, especially from the last active operation of the ACR field hospital deployed as a part of the ISAF mission in Kabul in 2007-2008, there emerged a requirement for more robust blood supply of troops. The reason was an unfulfilled assumption of smooth blood supply of the ACR foreign missions with use of supply flights. The air transportation method only is neither effective nor sufficient. The flying costs are high, brings problems with storing and product expiration arise, airlift can be busy, air transportation is not flexible and effective enough during emergencies and the whole process needs to meet strict legislative requirements and bureaucracy.
Although the medical staff of the ACR field hospitals was able to collect the whole blood on place several times in urgent extraordinary need, it was always an improvised solution without necessary sufficient technical background and fully educated personnel. This solution represented lot of risks and it could not be used systematically. The spectrum of available blood products was also inadequate, especially platelets (PLTs) were lacking.
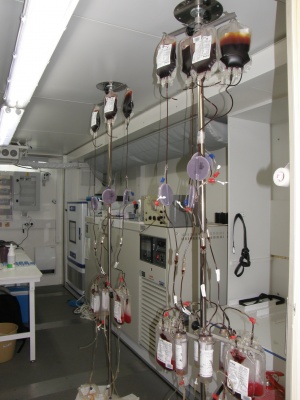
 FTU – view of technological part
FTU – view of technological part
With regard to experience of military medical services of some allied countries, especially in the Netherlands, the concept of a completely new specialized containerized transfusion unit was accepted. It enables to guarantee a sufficient amount of blood products for the field hospital under all circumstances in combination of all existing and applicable ways and methods. Crucial assignment was to guarantee of self-sufficiency in blood products supply of field hospital in missions in any case with three elemental components: RBCs, FFP and PLTs. In addition, blood supply system must be robust as most is possible and must avoid all known complication. Solution was an integration of a capability to receive blood products from the territory by air or ground transportation, the stock of frozen blood components (i.e. besides plasma also frozen RBC and PLT) and a capability of „walking blood bank“, i.e. collection of blood from blood donors in the place of deployment and safe production of blood products.
The special Field Transfusion Unit (FTU) was developed between 2011 and 2013 implemented for use in the ACR in 2014. The unit integrates all known and accessible possibilities of blood and blood products supply system: 1/ Delivery and storage of blood products through periodic supplies from the territory, 2/ The stock of frozen blood products (RBCs, PLTs and FFP) with a possibility of their thawing and reconstitution, 3/ Blood collection in the place of deployment and use of the fresh whole blood or a possibility of RBCs and FFP production for their consequent storage.
In the field hospital structure, the module is assigned to the cooperation with the biochemical and hematological lab and following operational-tactical requirements were determined during its development:
- FTU is designed for collection of blood, storage of blood products and thawing and reconstitution of frozen BP in providing health care during ACR operations. The module must fulfill all technical requirements of a field unit and its equipment must enable specialized activities according to necessary legislative regulations and simultaneously it must fulfill requirements for ability to be transported, manipulated and to be shockproof. The construction and technologies (wiring, water supply system, air-conditioning, heating, communication means etc.) have to meet combat efficiency requirements. With regard to the nature of the stored material, FTU must be equipped with an independent energy source enabling permanent operation without an external energy source connection. FTU must be able to operate separately on the reserve source during the external energy source failure.
- FTU has to be transported as a common storage container ISO 1C during transportation between stages of the field health care system, has to meet requirements for foreign mission support, for health care support of troops during their preparation and training in peacetime and during deployment as a part of the Integrated Rescue System of the Czech Republic (CR) in case of disasters.
Field transfusion unit – description and operation
- FTU – specifications
FTU is a medical module in the distensible container ISO-1C which is used for the production and storage of blood products and reconstitution of frozen blood components. From methodical and structural point of view, it is a part of the field hospital laboratory complement (together with biochemical and hematological lab and microbiological lab). There is a wide range of BP stored in FTU (suspended and leukodepleted packed red cells, fresh frozen plasma, frozen red cells and frozen platelets) in a quantity of a few hundred units an actual amount and range of which depends on a particular operational task. RBCs reserves are continuously refilled by supplies of fresh RBCs in a quantity and blood groups composition according to field hospital demands and operational task with use of supply flights. All blood products are sourced from territorial military blood bank, Department of Hematology and Blood transfusion, Central Military Hospital – Military University Hospital Prague (CMH) and derived from an unpaid volunteer donor pool. All donations are screened and tested in accordance with national and international guidelines. To minimize the risk of transmission of infection, blood is screened with serological tests for four targets (HBsAg, Anti-HCV, Anti-HIV ½+Agp24, syphilis) and with NAT for five targets (VHA, VHB, VHC, HIV, BV-B19). Cell products are leucodepleted, plasma is from low TRALI risk donor pool and for clinical use is released after 4 month quarantine with repeatedly negative infectious screening.
 Set of FTU and BHL-FH
Set of FTU and BHL-FH
In case of a mass casualty situation and high consumption of BP or a failure of regular supplies, frozen RBCs are used. Eventually, FTU enables to obtain not only the whole blood but also has capability to make separation of whole blood to RBCs and plasma by alternative collection of blood donors in the place of operation with use of special collection disposable sets.
The FTU capacity is 150 TU (transfusion units) of the whole blood, 150 – 250 TU of frozen units (RBCs, PLTs and plasma) – according to the storage method within the field hospital operational task and a situation in the place of deployment.
Functionally, FTU is attached to the biochemical and hematological laboratory (BHL-FH) module which besides basic biochemical, hematological, and serological examinations plays the role of the serving blood bank for clinical wards and of the clinical immunohematology lab for patients´ blood grouping and antibody screening, cross-matching. FTU and BHL-FH are equipped with modern information technologies and necessary laboratory and transfusion SW.
- The container
The FTU design and construction were implemented with use of the distensible container ISO 1C with the following basic parameters:
- The container is extendable by mechanical sliding of both sides (two persons within 30 minutes), a technological part is separated from a specialized one.
- The container is thermally insulated (except the technological part), dust-proof and water-proof.
- External dimensions of folded container: length x width x height = 6 058 mm x 2 438 mm x 2 438 mm.
- External dimensions of unfolded container: length 6 058 mm, width max. 5 000 mm.
- Container operation at external temperatures: from -32°C to +49°C.
- Container storage at external temperatures: from -33°C to +58°C.
- FTU - equipment
The FTU built-up area includes necessary equipment for storage of frozen and fresh BP, for thawing and reconstitution of frozen BP (RBC and PLT), for blood donors collection and subsequent processing of blood in field conditions, when all hygienic and legislative requirements are met.
Equipment for BP storage:
- ultra low freezer Sanyo MDF 547 (487 l, up to -86°C),
- backup CO2 system for ultra low freezer (up to 20 hours function)
- blood refrigerator Dometic BR 250G,
Equipment for thawing and reconstitution of frozen RBC:
- automated cell processor Haemonetics ACP 215 – 3 pcs
- thermal water bath with shaker Tool – 1 pc
- thawing bath Tool – 1 pc
- sterile tube connecting device TCD B40 – 1 pc
Equipment for blood collection and processing:
- blood collection mixer Docon Macopharma – 6 pcs
- folding donor chairs LMB – 6 pcs
- tube sealer Macoseal Mobile Macopharma - 2 pcs
- hemoglobin meter Hemocue – 1 pcs
- stands and holders for ErySep® sets with a hollow fiber filter – for 8 disposable sets
Laboratory equipment for testing of collected blood:
- Saxo reader DiaMed – blood grouping + antibodies screening
- Mini Vidas BioMerieux – infectious agent screening (in BHL-FH)
Equipment for monitoring of:
- temperature and humidity in the space,
- CO2 concentration in the space
- temperature in cooling and freezing boxes
The special transfusion SW:
 FTU – overall view of interior
FTU – overall view of interior
SW enables all necessary operations, i.e. blood donors registration, their admission to blood collection, recording of collection, including data import from blood collection mixers, recording of BP production, import of lab results from analyzers, laboratory testing recording, blood products releasing, BP labeling, BP inventory control and BP expedition.
- Frozen blood products and related methods and procedures
Frozen blood components are produced and frozen at the Department of Hematology and Blood Transfusion CMH and they are transported to the place of FTU deployment or to the field hospital in an adequate quantity inside boxes with dry ice.
4.1 Frozen red cells
RBCs are frozen in 40% glycerol as cryoprotective agent in -80°C and maintained should be at less than – 65°C, Cells are processed in a fully closed, semi-automated cell processor Haemonetics ACP 215. Before use they are deglycerolised with 12% NaCl, washed with 0.9% NaCl and 0.2% glucose, and suspended in a citrate-containing nutritional solution AS-3 (Nutricel). Three units of red cells can be thawed and reconstituted every 90 -120 minutes. Regular processing allows liquid blood stores to be replenished to maintain an immediately available supply. The shelf-life of thawed red cells is 21 days at 2 – 6°C.
4.2 Frozen platelets
Leukodepleted, volume-reduced frozen PLTs are obtained by apheresis from a single donor, cryoprotected in a 4% – 6% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and stored at less than – 65°C. Each unit contains about 300 × 109 platelets. The freezing process induces some morphological and functional changes and compared with liquid-stored platelets, are frozen platelets “preactivated” which has the clinical consequence of faster creation of primary clot. An expiration of these platelets in frozen state is up to 4 years. Used platelets are only of blood group 0 and they are reconstituted in thawed plasma of blood group AB. The reconstitution process of frozen platelets is very simple, it does not need washing and removing of DMSO, the time for the process does not exceed 30 minutes. Thawed PLTs is required to use within 6 hours.
4.3 Fresh frozen plasma
 BHL-FH – view of interior with analyzer Mini Vidas BioMerieux
BHL-FH – view of interior with analyzer Mini Vidas BioMerieux
It is a standard product which was also used in the former concept based on regular supplies of field hospitals from the territory. The used plasma is prepared either from whole blood or from plasma collected by apheresis, frozen within 6 hours after collection that adequately maintain the labile coagulation factors in a functional state. Plasma units for clinical use are prepared only from selected blood donors, meets standards of reduced risk of TRALI (Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury). A shelf life of frozen plasma stored at temperature -25°C and lower is 3 years. Frozen plasma can be in FTU conditions also produced from own blood collection in the place of deployment – see below.
- Blood donors collection and BP production in the place of deployment - „walking blood bank“
Equipment of the container and collaborating BHL-FN enables to carry out sophisticated collection of the whole blood from blood donors directly in the place of deployment, including subsequent laboratory testing according to the minimal territorial standards, i.e. examination of blood groups, unregularly anti-erythrocytes antibodies and screening of serological infection markers (HBsAg, anti-HCV, anti-HIV, and syphilis – TPHA). NAT screening of blood donors in field conditions is not possible at the moment.
The collected whole blood can be immediately used for transfusion as the “fresh whole blood” after laboratory testing and releasing. If required to refill reserves, it can be processed on red cells and plasma. The special blood collection disposable set ErySep® with integrated hollow fiber filter is used for subsequent processing of the whole blood. ErySep® is a blood separation system, which separates whole blood into its components without centrifuge or extractors in high quality. When the set with collected blood is hung on the special stand, the whole blood is firstly leukodepleted and subsequently erythrocytes and plasma are separated only due to the gravity. RBCs are stored under standard conditions in 2-6°C for 42 days, plasma is quickly frozen in the deep-freezing box and then stored at temperature -25°C and lower.
- Staffing of the FTU + BHL-FH
The deployed FTU, which is mostly supposed to operate in assembly with BHL-FH, must be staffed with well trained professionals because the processing of frozen blood products, i.e. their thawing and reconstitution, represents a group of highly specialized skills which require ability to operate relatively complicated technology. There is a similar situation in expertise in blood donors collection and blood processing. That is why staffing requirements are defined as follows:
- 2 qualified medical laboratory technicians who master all ACR field hospital laboratory matters and are able to operate all devices of FTU and BHL-FH
- the field hospital must be staffed with 4-6 nurses who are educated and periodically trained in problems of blood donors and blood processing
- an authorized field hospital physician takes methodical and specialized responsibility, he must be educated and trained in problems of laboratory hematology, biochemistry and transfusion services. He must be an expert in internal medicine, surgery, ICU or urgent medicine. This authorized field physician simultaneously plays the role of the field hospital transfusiologist.
- FTU logistic assignment and deployment
FTU is primarily included in the field hospital structure, it is attached to a tent corridor connected with field hospital distribution systems. It is situated next to BHL-FH with which it has the common data interface and SW for related activities; some laboratory devices are connected directly to FTU.
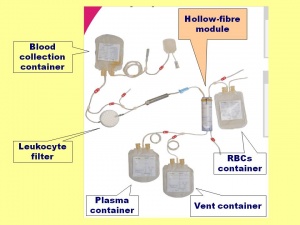 Disposable set ErySep®
Disposable set ErySep®
The FTU priority destination is to support medical facilities of the combat health care system (Role 2E/3) during ACR components deployment in missions, to provide ACR peacetime health care support, including its preparation and training.
Separately or together with BHL-FN, FTU can be integrated into the Czech Republic Integrated Rescue System during disaster management.
In case of international collaboration, FTU can be deployed (separately or together in set with BHL-FN) in the frame of alliance medical task force (alliance field hospital) as a specialized element to supplement operational capabilities of a coalition partner. The facility can be provided with trained professional staff or without the staff on condition that training of alliance team (alliance country) will be provided in the Czech Republic.
Conclusion
The new blood supply concept of the ACR troops based on FTU connected with BHL-FH represents nowadays the most complex solution of blood products field supply system within NATO countries. It was stated at the COMEDS NATO expert working group for blood transfusion, “Medical Blood Advisory Team“ in May 2013.
Introducing 3 pillars of blood supply system (supply from the territory, frozen blood components, whole blood collections in the place of deployment) for the need of field hospitals ensures a maximal system robustness enabled by up-to-date available transfusion procedures. Availability of platelets is an exceptional solution. A majority of NATO medical services and others do not have this possibility at all. Introducing the whole blood processing with use of separation through the hollow fiber is also unique. This system enables the production of adequate red cell and plasma for subsequent storage.
Summary
 Separation of collected whole blood
with use of disposable set ErySep®
Separation of collected whole blood
with use of disposable set ErySep®
Blood substitution and blood supply are permanent strategic and logistic problems of military medical services across the world arising from the blood, which is a biological drug, has a limited shelf life and needs special conditions for transport and use. The availability of sufficient blood is the crucial issue of military medical service, because exsanguinating hemorrhage is the major cause of death in military operations. The concept of blood supply of the Army of the Czech Republic (ACR) field hospitals (FH) operating in foreign missions was based on periodic delivery of blood products, usually in four-week intervals with use of supply flights. Based on long-term experience, there emerged a requirement for more robust blood supply of troops. In 2011 – 2013, the special field transfusion unit (FTU) has been developed. FTU integrates all known and accessible possibilities of blood and blood products supply: 1/ Delivery and storage of blood products through a periodic supplies from the territory, 2/ Stock of frozen blood products (RBC, PLT and plasma) with a possibility of their thawing and reconstitution, 3/ Blood collection in a place of deployment, use of the fresh whole blood or a possibility of RBC and plasma production for consequent storage. ACR FTU, together with the ACR field lab unit, is currently the most complex solution for securing a healthy supply of blood and blood products during field operations within the NATO countries.
Author:
LtColonel Milos BOHONEK, MD, PhD
Central Military Hospital – Military University Hospital, Prague
Department of Haematology and Blood Transfusion
Czech Republic
Date: 12/03/2018
Source: Medical Corps International Forum (4/2015)











